Longevity
Give Aging a Little Shock with Heat Shock Proteins
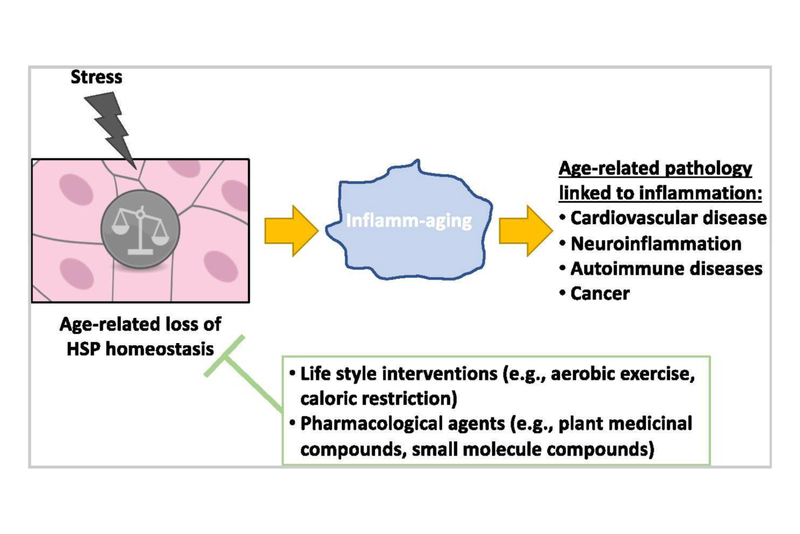
In addition to NAD+ and cellular senescence, heat shock proteins (HSPs) are emerging as a key area of interest for scientists who study the biological mechanisms of aging and longevity. These remarkable cellular protectors have been linked to enhanced stress resistance, improved cellular function, and ultimately, increased lifespan by altering the progression of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, and autoimmunity.
Heat shock proteins are a group of molecular chaperones that play a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. They are called "heat shock" proteins because their expression is induced in response to stressors like heat, toxins, infections, and other environmental challenges. However, their significance extends far beyond merely responding to thermal stress.
Key Roles of Heat Shock Proteins
- Protein Folding and Stability: HSPs assist in the proper folding of proteins, preventing misfolding and aggregation. This ensures that cellular proteins maintain their structural integrity and function optimally.
- Cellular Stress Response: HSPs are activated in response to various stressors, helping cells cope with adverse conditions. This stress response is vital for cellular survival and resilience.
- Anti-Aging Effects: Research suggests that the upregulation of heat shock proteins may contribute to delaying the aging process by preserving cellular function and reducing the accumulation of damaged proteins.
Similar to increasing NAD+ and reducing senescent cells, activating HSPs involves strategies such as exercise and caloric restriction. Furthermore, heat exposure and certain nutrients can boost your HSPs, as detailed below.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, including aerobic exercise, high-intensity interval training (HIIT), and resistance training, has been shown to stimulate the production of HSPs. Exercise induces a controlled cellular stress, prompting the body to upregulate protective mechanisms, including heat shock proteins.
- Caloric Restriction: Studies have suggested that caloric restriction may enhance the expression of HSPs. Adopting a balanced and nutrient-dense diet while limiting calorie intake might positively impact longevity through the activation of these protective proteins.
- Sauna and Heat Therapy: Exposure to heat, such as through saunas or hot baths, triggers the heat shock response. This gentle stressor can stimulate the production of HSPs, promoting cellular health and resilience.
- Polyphenol-Rich Foods: Certain compounds found in fruits, vegetables, and teas, such as resveratrol and quercetin, have been associated with increased HSP expression. Including a variety of colorful, plant-based foods in your diet may contribute to promoting heat shock protein production.
Image courtesy of the National Library of Medicine.
More News
-
New!
More

Strength Training and Progressive Overload for Longevity
While the pillars of longevity include lifestyle factors such as sleep, social connection, diet and environmental factors, exercise may be the most important component for improving our healthspan.
-
New!
More

Environmental Sustainability at Vail Health
With a strong focus on the connection between human and environmental health, Vail Health’s Environmental Sustainability department has been committed to becoming more energy efficient, diverting more waste from landfill, and reducing water consumption throughout its facilities. Their efforts are paying off.
-
More

Simple Tips for Extending Your Healthspan at 60+
As we grow older, it’s essential to adjust our habits to not only add years to our lives but also to enhance the quality of those years. One of the best ways to extend your healthspan is by embracing the Five Pillars of Health, which focus on key areas of well-being that support physical, mental, and emotional health.
